Introduction
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of almost all modern electronic devices. They serve as the structural foundation and electrical interconnection medium for electronic components, ensuring the entire system functions as designed. Within the diverse family of PCBs, Flexible Printed Circuits (FPCs) stand out due to their thin, bendable, and lightweight properties. These flexible circuits are widely used in industries such as automotive, medical, consumer electronics, and telecommunications.
One important variation within this field is the double-sided FPC—a flexible printed circuit with conductive traces on both the top and bottom layers. Unlike single-sided FPCs, which have circuitry only on one side, double-sided versions allow for more complex routing, increased component density, and improved functionality without expanding the circuit’s footprint.
But what exactly makes a PCB "double-sided"? In essence, it’s the presence of two conductive layers connected by vias, enabling signals and power to travel between the two sides. This increases design flexibility, accommodates more components, and often improves performance in high-density or multifunctional devices.
When exploring the question “Can PCBs be double-sided?”, the short answer is yes—and not only can they be, but double-sided PCBs are a cornerstone in modern electronics manufacturing. In the flexible PCB category, this means engineers can combine the mechanical advantages of FPCs with the electrical benefits of two-sided layouts, creating solutions that are compact yet powerful.
What Is a Double-Sided FPC and How Is It Made?
A double-sided FPC is a flexible printed circuit board that has copper traces on both its top and bottom surfaces, connected through plated through-holes or vias. This configuration allows signals to be routed between layers, enabling more complex designs without increasing the overall size of the circuit. The ability to fold or bend the board makes it highly suitable for compact spaces, such as inside automotive steering wheel control modules or wearable devices.
The manufacturing process begins with a flexible base material, usually polyimide, known for its high heat resistance and excellent electrical properties. A thin copper foil is laminated on both sides of the substrate. Through photolithography, etching, and plating, circuit patterns are defined on both surfaces. Vias—tiny holes drilled through the substrate—are plated with conductive material to create electrical connections between the two copper layers.
Key steps include:
Substrate Preparation – Selecting high-quality polyimide or PET for flexibility and heat resistance.
Copper Lamination – Applying copper foil to both sides of the substrate.
Pattern Imaging – Using photoresist to define the circuitry layout.
Etching – Removing excess copper to reveal the designed traces.
Drilling and Plating Vias – Creating interconnections between layers.
Surface Finishing – Applying finishes like ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold) for improved solderability.
Component Assembly – Mounting and soldering components on both sides if required.
By enabling component mounting on both surfaces, double-sided FPCs effectively double the usable surface area without increasing the footprint, a major advantage in high-density electronics.
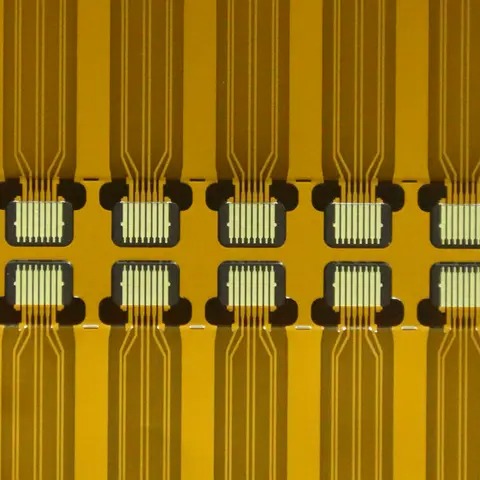
Advantages of Double-Sided FPC Over Single-Sided Designs
Double-sided FPCs offer multiple benefits that go beyond the capabilities of single-sided circuits. The ability to place conductive traces on both sides creates room for more complex designs, additional components, and enhanced functionality.
Higher Component Density
With traces on both sides, designers can pack more functionality into a smaller space. This is particularly valuable in applications like automotive steering wheel switches, where space is extremely limited but functionality requirements are high.
Improved Electrical Performance
Having two conductive layers allows for shorter signal paths and optimized grounding, which can improve signal integrity, reduce noise, and enhance overall electrical performance.
Greater Design Flexibility
Double-sided layouts enable engineers to separate high-power and low-power circuits or isolate sensitive analog signals from noisy digital lines. This separation can significantly improve device reliability and performance.
Cost-Effectiveness for Complex Designs
While the initial production cost of double-sided FPCs is higher than that of single-sided boards, the overall system cost can be reduced because the same functionality might require fewer separate boards or interconnections.
Applications of Double-Sided FPCs in Modern Industries
Double-sided FPCs are used in a wide range of industries due to their versatility and performance advantages.
Automotive Industry – In steering wheel controls, infotainment systems, and dashboard electronics, double-sided FPCs provide high reliability in a compact form factor. Their flexibility allows them to fit within curved or moving parts without compromising durability.
Consumer Electronics – Smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices benefit from the ability to route signals in tight spaces while maintaining high-speed data transmission and power delivery.
Medical Devices – Double-sided FPCs can be integrated into compact diagnostic tools, surgical instruments, and wearable health monitors. The flexibility ensures comfort and reliability, especially in patient-worn applications.
Industrial Equipment – Robotics, sensors, and control systems often require compact, high-density circuits with robust mechanical and electrical performance. Double-sided FPCs deliver on these requirements while allowing for creative mechanical integration.
Comparing Single-Sided and Double-Sided FPCs
| Feature | Single-Sided FPC | Double-Sided FPC |
| Copper Layers | 1 | 2 |
| Component Placement | One side only | Both sides |
| Circuit Density | Low | Medium to High |
| Design Complexity | Simple | Complex |
| Electrical Performance | Basic | Enhanced |
| Cost | Lower | Higher initial, cost-effective for complex designs |
| Applications | Simple interconnections, basic devices | Advanced electronics, compact multi-function devices |
From this comparison, it’s clear that while single-sided FPCs are suitable for straightforward applications, double-sided FPCs are the choice for projects requiring more advanced functionality in limited space.
Common Questions About Double-Sided PCBs and FPCs (FAQ)
Can all PCBs be made double-sided?
Not all PCB applications require a double-sided configuration. For simpler devices, a single-sided PCB or FPC may be sufficient. However, for more complex devices where space and performance are critical, double-sided designs are an optimal choice.
Are double-sided FPCs more expensive?
Yes, they generally cost more to manufacture than single-sided versions due to additional materials, processes, and complexity. However, they can reduce overall system costs by consolidating multiple circuits into one.
How are the two sides connected in a double-sided FPC?
Electrical connections between the two layers are achieved through plated vias, which are small holes drilled through the substrate and filled or coated with conductive materials.
Do double-sided FPCs have a shorter lifespan?
Not necessarily. When designed and manufactured with quality materials and processes, their lifespan can be equal to or greater than that of single-sided boards.
Conclusion
In fact, double-sided FPC technology is not just possible—it’s an essential part of modern electronics manufacturing. By combining the mechanical flexibility of FPCs with the electrical advantages of two-layer designs, engineers can create compact, reliable, and high-performance circuits for an ever-growing range of applications.
As devices continue to get smaller yet more powerful, the demand for double-sided FPCs will likely increase. Their ability to maximize space utilization, improve electrical performance, and support complex designs ensures they will remain a critical technology in industries from automotive to healthcare. For engineers and product designers seeking innovative solutions, double-sided FPCs represent both a practical choice and a gateway to future design possibilities.





















